The Mikon Rule Server is a potent add-on to the Mikon Application Servers. The first version was developed as a generic tool to substitute complicated customised interfaces and to solve issues that the Mikon Calculator could not solve. For instance, can SQL selects be used in filters and actions/calculations. Over time more functionality has been added for Mikon batches/genealogy, starting parameterised external operations (like SQL commands in the Mikon database) or any program in a command file for instance (like an excel)
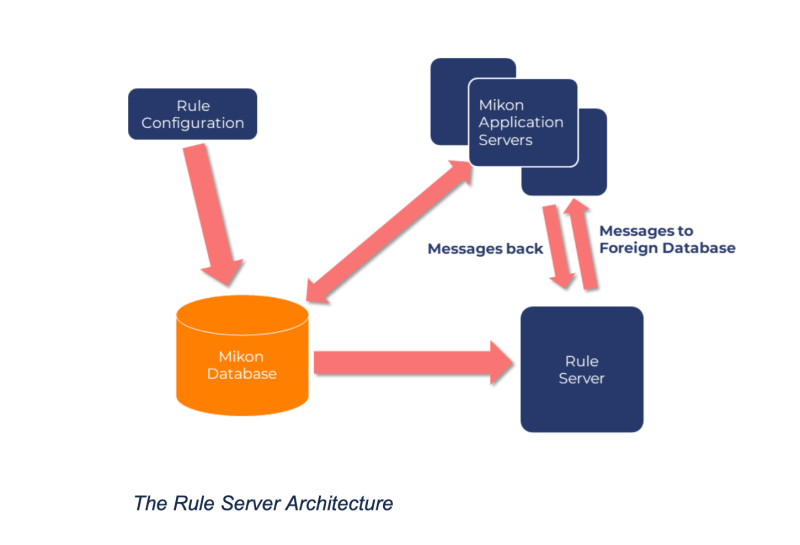
The Mikon core architecture is based on messages that initiate inserts, updates, and deletes signals, batches, and genealogy. The Rule Server is designed to act on these messages to transform and generate new messages based on a custom rule server configuration.
Rule Server Architecture
The Rule Server is implemented as a "Foreign Database Server" that listens to messages passed to a Foreign Database from the Mikon Application Servers (ddmanager) and acts according to the rule configuration passing new messages back to the Mikon Application Servers.
It can also be used as a configurable middleware when making interfaces with other systems that do not have the same concepts of Mikon building blocks as batches, signals and genealogy.
Rule Server Configuration
A rule consists of
a trigger (like a signal value, batch)
one or more filters/validations and
one or more actions that have to be configured.
There are two types of filters.
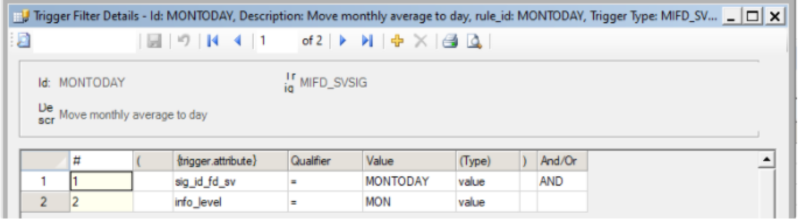
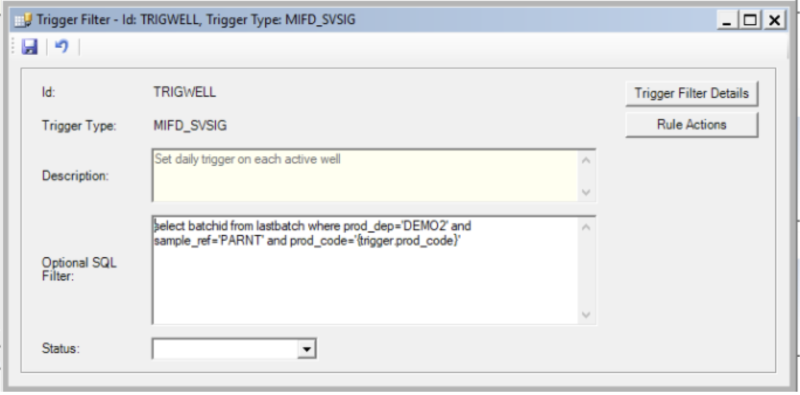
Trigger Filter Details
The filter detail defines a set of attributes on the trigger that qualify for the rule and associated actions to be performed. The filter is constructed as a complex filter that can use parentheses and Boolean operators. The filter could be on constant values or dynamic values from the trigger. Notice that several trigger signals could share the same rule by sharing the same sig_id_fd_sv (MONTODAY in the example) in the regular Signal configuration / Accumulation.
Optional SQL filter
to create additional filters on a rule trigger before performing any actions. It could be a SQL SELECT statement. If the SQL statement returns one or more rows, the SQL is considered TRUE, and the Rule actions will be executed. The SQL filter is processed after Trigger filter details.
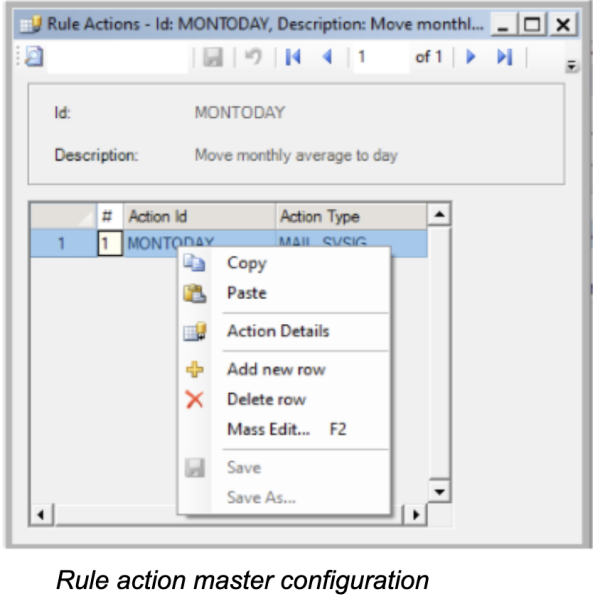
Rule Actions Setup
Action is usually a standard Mikon message (like a signal, batch) back to the Mikon server. The actions could also be any SQL command (also updates/deletes) or any OS command (like starting another program in a command file like an excel program).
In the action details configuration, relevant parameters for the message types are described. The parameters could be value(constants), trigger values, SQL-command (select). The examples below are sending a Mikon message back to the Mikon servers.
Action Type
This identifies the action type to be performed. Valid options are:
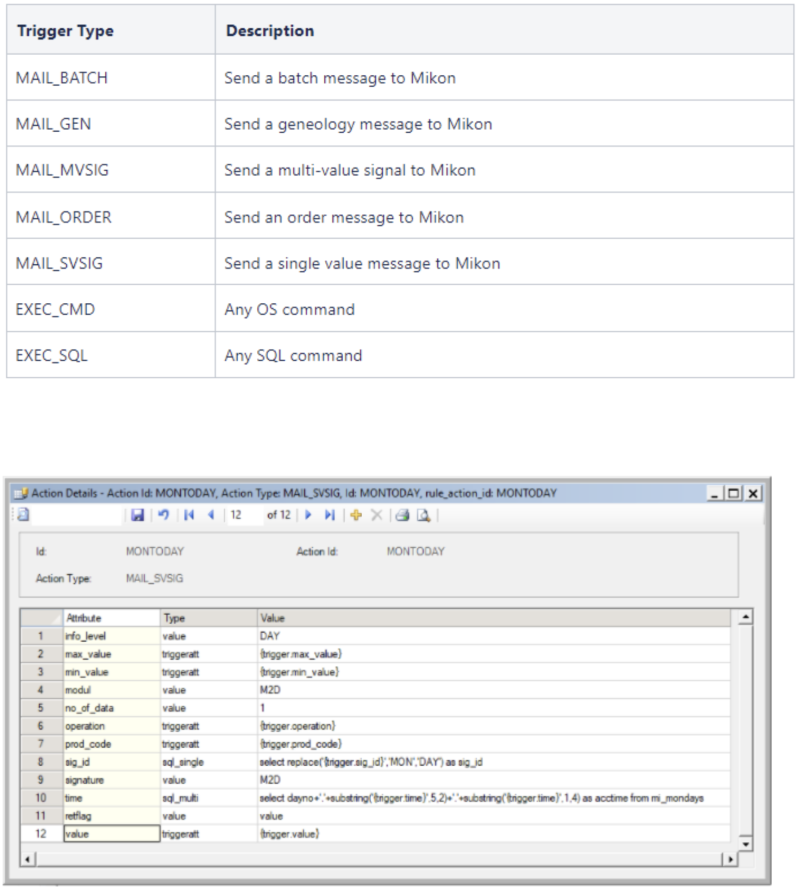
Rule action detail configuration
The SQL command could use any table or view accessible from the Mikon database
Rule server examples
Example 1. A type of «event» trigger signal online from the process or calculated as a Mikon signal, could be the indication of the start of a new batch with two actions. Ending the current batch and setting up a new batch with an estimated stop time.
Example 2. A type of «event» trigger signal online from the process or calculated as a Mikon signal, could be the indication of setting up a new genealogy link to the current batch in a «neighbour» department.
Example 3. Copy signal values from a higher Mikon level to a lower Mikon level which is not possible with the Mikon Calculator. Like a Monthly daily budget that should be copied to a DAILY level.
Example 4. Copy a signal value for a blank product to all defined products. Often used as a “dummy trigger” in Mikon product-related equations.
Example 5. An event-driven activation of a report like a printout of a QR code.
For more information please check Mikon Documentation: Mikon Server / Rule Server Development Guide